Figure 2.1
Terminal Services allows IT departments to install applications on a central server. For example, instead of deploying database or accounting software on all desktops, the applications can simply be installed on a server and remote users can log on and use them via the network. This centralization makes upgrading, troubleshooting, and software management much easier.
However, since all terminal clients share the server's network, it becomes difficult to monitor/filter individual users internet usage because most internet monitoring/filtering products only monitor/filter internet activities based on ip addresses or MAC addresses.
This tutorial will guide you to monitor/filter terminal service users with WFilter's "account monitoring" and "proxy server" features.
Network topology diagram:

Please notice: WFilter shall not be installed in the terminal server.
First you need to enable "Account Monitoring".
If you have an available active directory, you can integrate WFilter with your Active Directory.
If not, you also can enable "WFilter Local Account" to monitor/filter by users.
For more details, please check: How to do monitoring/filtering based on user accounts?.

Check "Enable Proxy" in "System Settings"->"Proxy Settings", and enable "User Authentication", as in below figure:
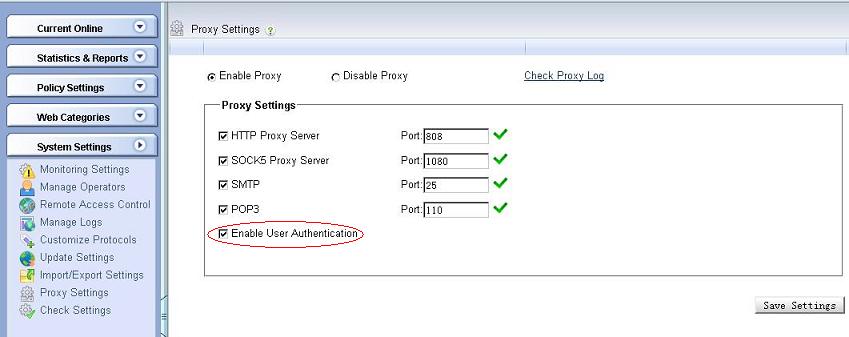
For WFilter to monitor terminal client users, please check below steps:
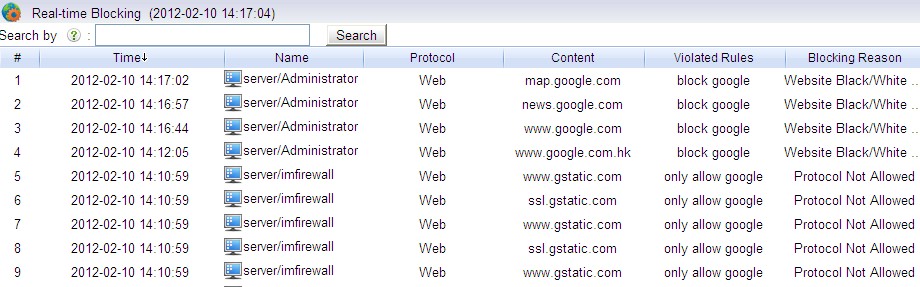
Now, each activity is associated with an username:
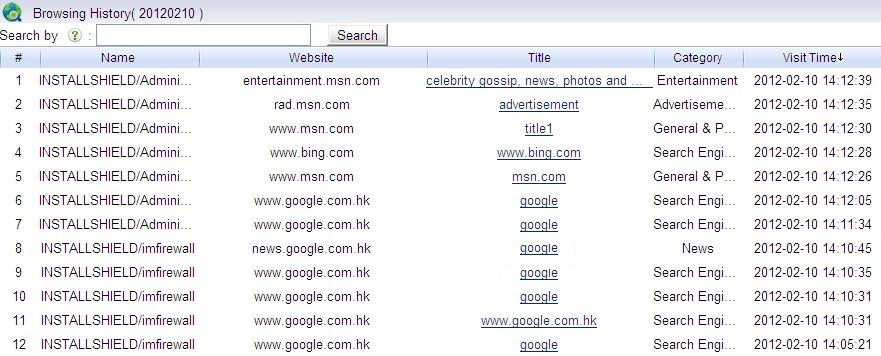
Each client is applied with its own blocking policy: